IPv6
More > Network > IPv6

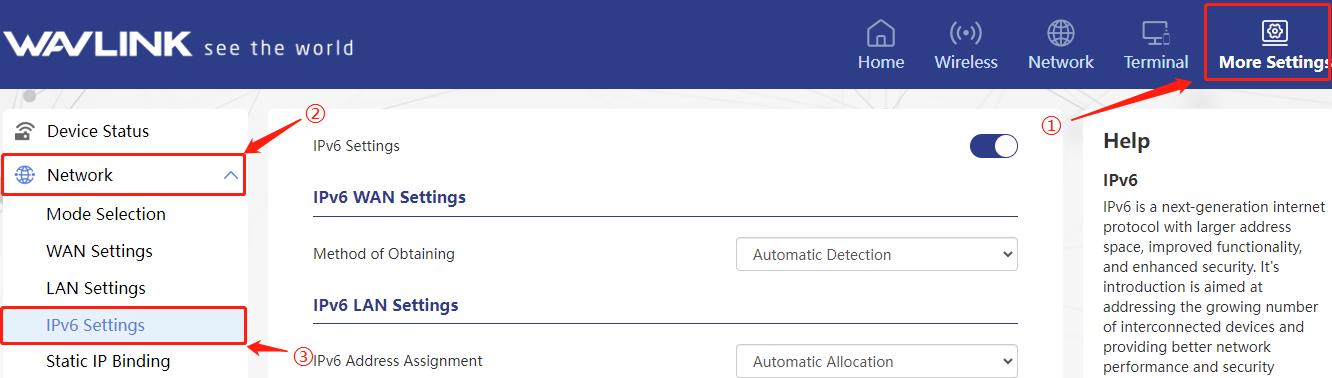
Advanced > IPv6 Settings


IPv6 is a next-generation internet protocol with larger address space, improved functionality, and enhanced security. Its introduction is aimed at addressing the growing number of interconnected devices and providing better network performance and security.
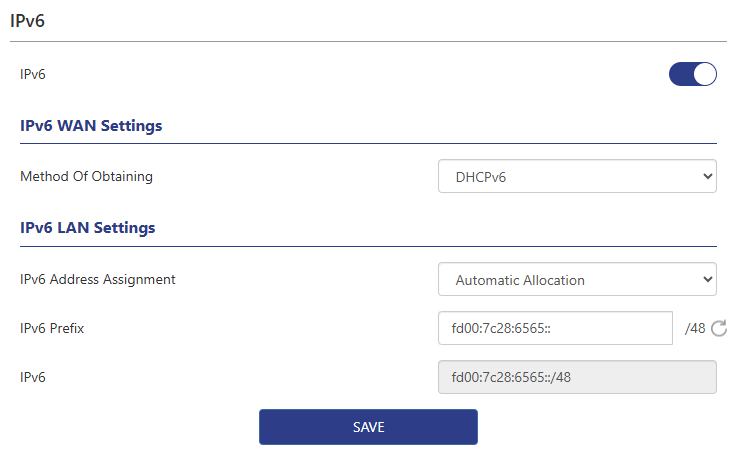
IPv6 WAN Settings
The method of obtaining IPv6 can vary depending on the network environment and provider support. Here is a brief description and differences between the different acquisition methods.
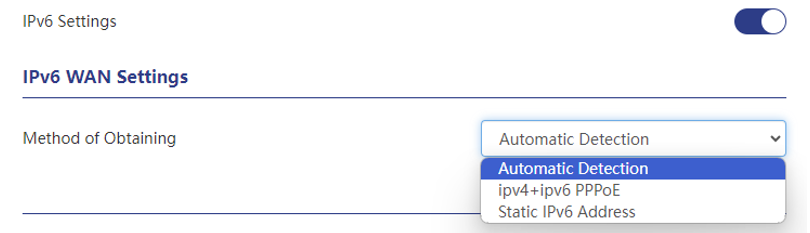
Configure IPv6 you should check these :
Check network support : First, make sure your network environment supports IPv6. You can contact your ISP or administrator to confirm whether they offer IPv6 connectivity.
Router configuration : Enter the router's management interface and find the IPv6 configuration option. You can choose to enable IPv6 and select the appropriate IPv6 connection type. Save and apply the settings.
Device configuration : Once your router is configured, you need to configure IPv6 on the device.In your device's network settings, you can find the IPv6 option and enable it. The device will automatically obtain an IPv6 address, or you can manually configure an IPv6 address.
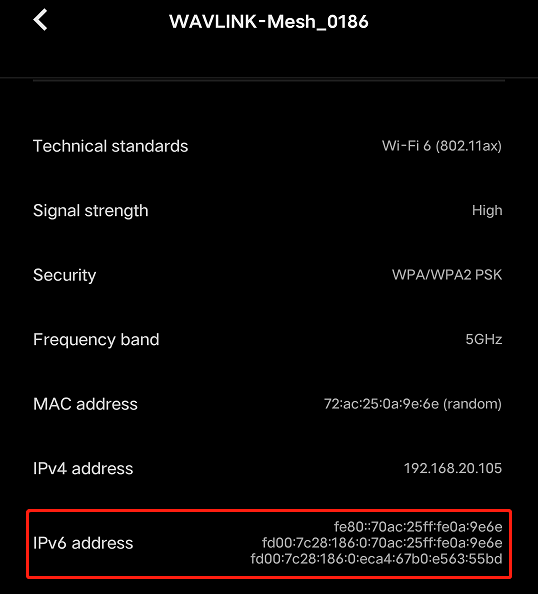
If you have enabled the IPv6 service, we provide two examples to help you check your IPv6 address.
If you use a mobile phone to connect to the router WiFi, you will see the IPv6 address assigned by the router to the mobile phone in mobile phone Settings > WiFi settings.
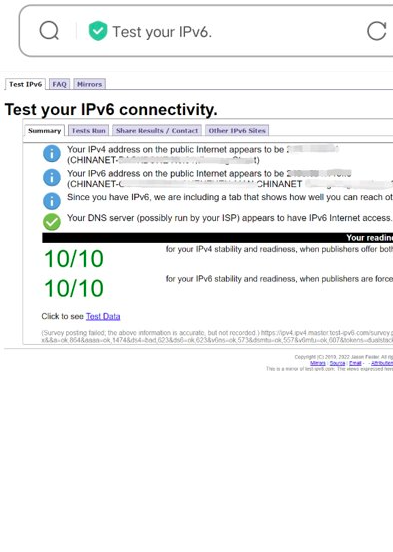
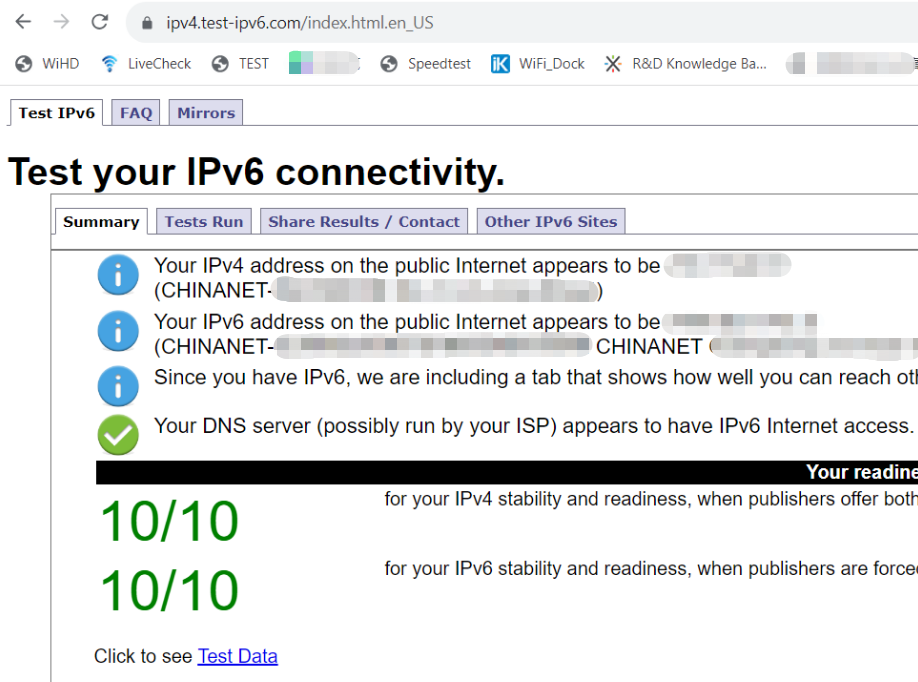
You can check whether the IPv6 network is successfully enabled by visiting the IPv6 website (http://www.test-ipv6.com).
If you are using a computer, you can type "win  + R" on the keyboard at the same time, enter "cmd" in the pop-up search box and click "Enter".
+ R" on the keyboard at the same time, enter "cmd" in the pop-up search box and click "Enter".
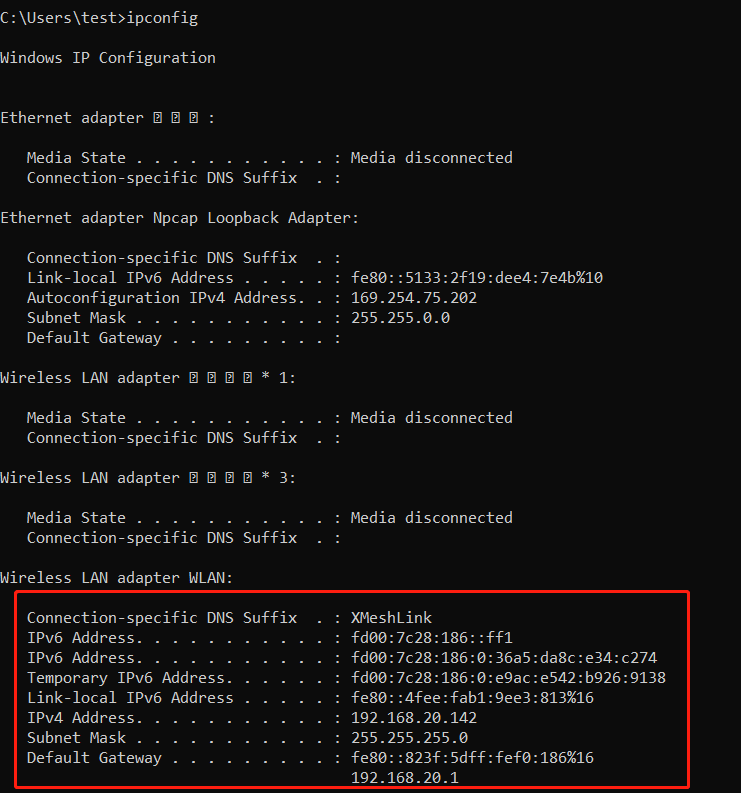
You can check whether the IPv6 network is successfully enabled by visiting the IPv6 website (http://www.test-ipv6.com).
Automatic Detection
This method is the most common and simple way to obtain an IPv6 address by automatically detecting the network environment. When you connect to an IPv6-enabled network, your device automatically obtains an IPv6 address. This method generally works on home or public networks and requires no special configuration.
IPv4+IPv6 PPPoE
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol Over Ethernet) is a protocol used to establish network connections. IPv4+IPv6 PPPoE is a method of obtaining both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses through a PPPoE connection. It can be used in networks that support PPPoE, such as network connections provided by some broadband access service providers (ISPs).
Note
IPv4+IPv6 broadband dial-up is to reuse the IPv4 dial-up link. It will only be enabled when the IPv4 Internet access method is also broadband dial-up. After enabling, IPv6 will use the IPv4 account and password for dialing, and there is no need to manually enter the IPv6 broadband account and password. Please note that enabling this function requires operator support. Please choose whether to enable it correctly according to the actual situation.
1 . Open the browser, enter wavlogin.link , and enter the password to enter the router management page.
2 . Click " More > Network > IPv6 ". Enable the IPv6 function and select IPv6 WAN acquisition method as IPv4+IPv6 broadband dial-up.
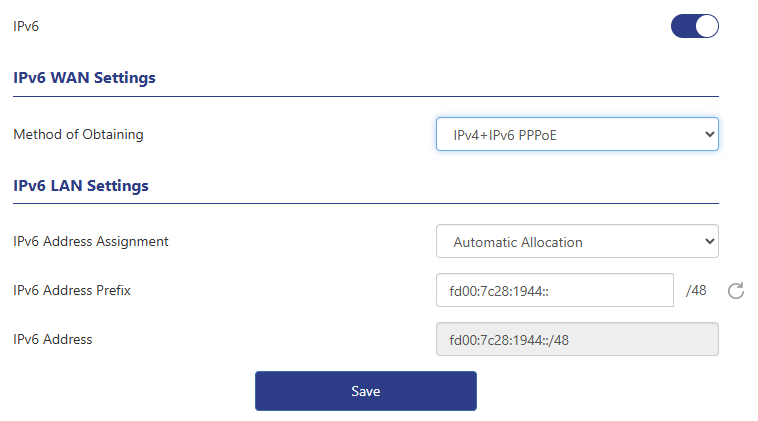
3 . Set up IPv6 LAN. The default IPv6 address allocation method is automatic allocation, which can also be modified as needed. If automatic allocation is selected, an IPv6 address will be dynamically allocated by the operator directly; if SLAAC is selected, the router will automatically generate an IPv6 address based on the routing announcement.
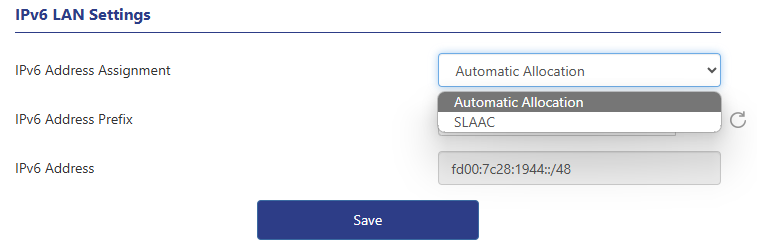
About IPv6 address prefix
Manual modification is supported. If you want to restore the default value, click the refresh button on the right side of the prefix box to restore the default value.
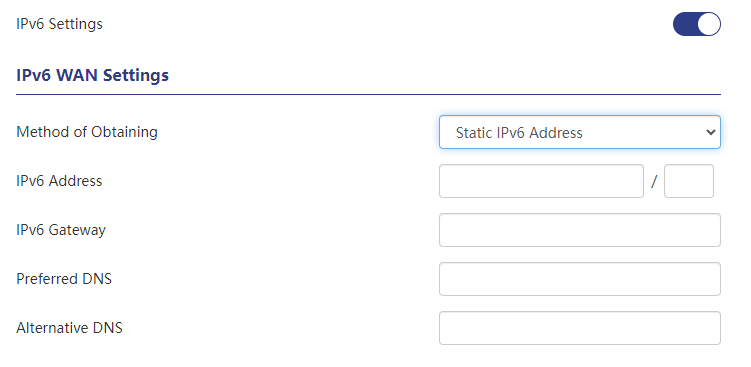
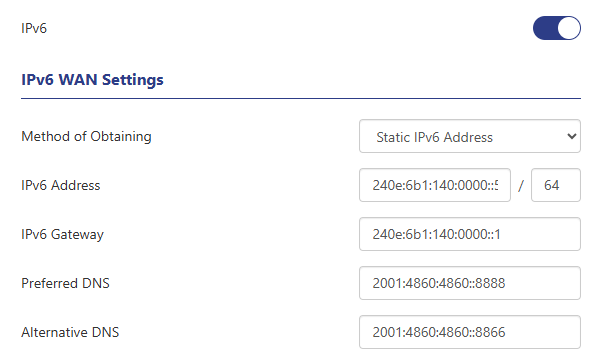
Static IPv6 Address
A static IPv6 address is a fixed IPv6 address that you configure manually. When using this method, you need to manually enter network configuration information such as IPv6 address, subnet prefix length, default gateway, and DNS server. This method is usually suitable for specific purposes that require a fixed public IPv6 address, such as servers or network devices.
Example :
1 . Open the browser, enter wavlogin.link, and enter the password to enter the router management page.
2 . Click "More > Network > IPv6" to enable the IPv6 function. Select the IPv6 WAN acquisition method as a static IPv6 address, and use the fixed IPv6 address provided by the operator to access the Internet. The subnet prefix length, gateway, DNS server and other Internet access parameters are also provided by the operator. Enter the IPv6 address, gateway, DNS server.
3 . After the settings are completed, click Save, wait for the configuration to take effect, and refresh the page to re-enter the page.
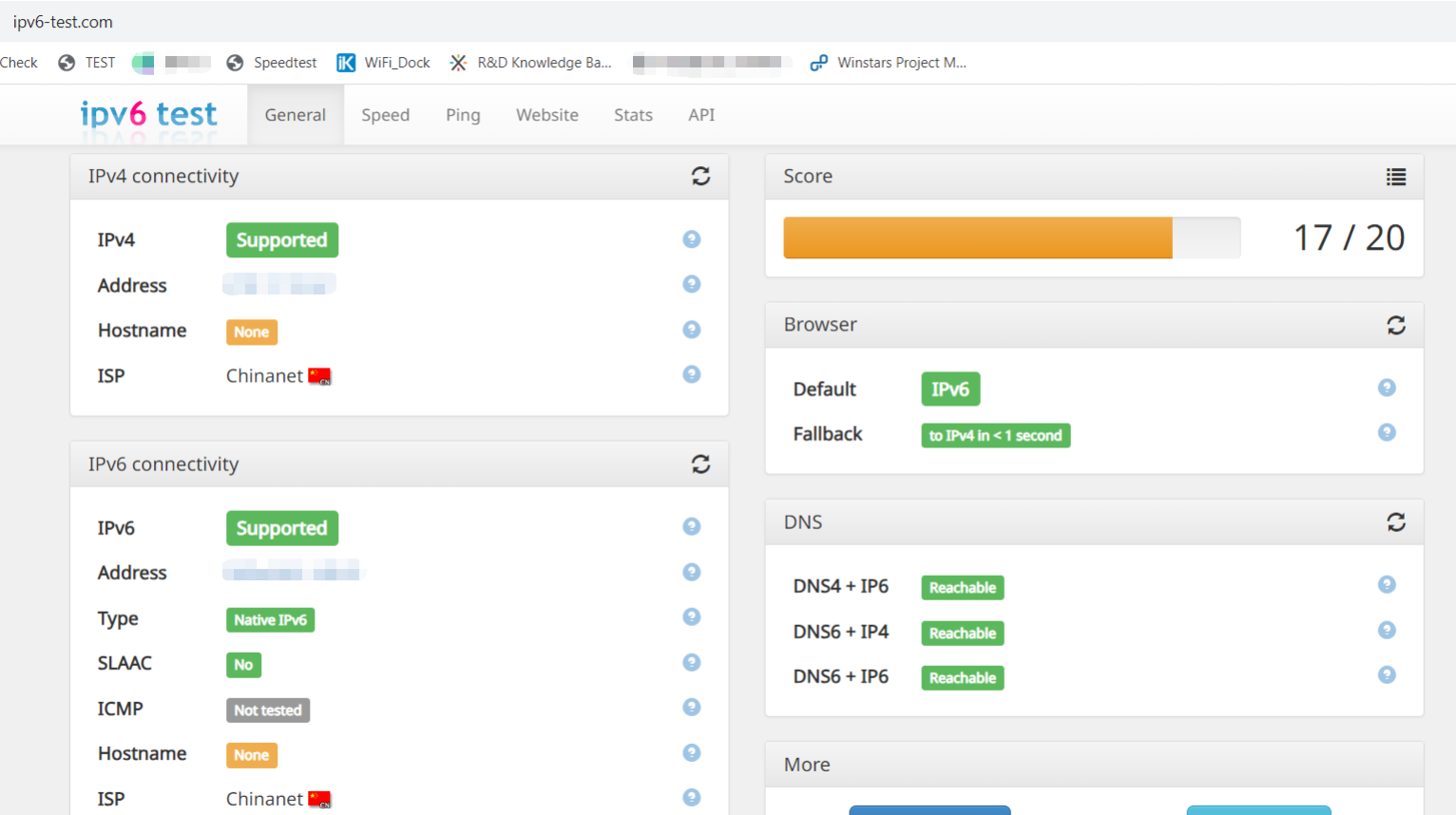
Open the browser and enter http://ipv6-test.com in the address bar to visit the IPv6 test website.
The difference between these methods is how the IPv6 address is obtained and the complexity of the configuration. Automatic detection is the simplest way and works in most cases. IPv4+IPv6 PPPoE requires the PPPoE username and password in the network settings. Static IPv6 addresses require manual configuration of detailed network information.
Which method to use depends on your network environment and your service provider's support. If you are unsure, it is recommended to contact your network service provider or administrator for accurate configuration information and recommendations.
IPv6 LAN Settings
IPv6 LAN addresses can be obtained through Automatic Allocation and SLAAC (Stateless Address Autoconfiguration). The uses and differences between these two methods are as follows :
Automatic Allocation
In automatic allocation mode, IPv6 LAN addresses are automatically allocated by network devices or routers to devices connected to the network. This method usually uses the DHCPv6 (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6) protocol for address allocation. After the device is connected to the network, it will automatically send a DHCPv6 request to the router, and the router will assign an available IPv6 address to the device.
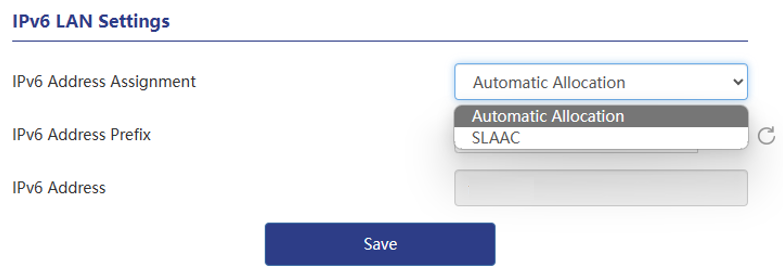
To use automatic allocation, you need to ensure that there is a router or device in the network that supports DHCPv6 and that the DHCPv6 server has been configured correctly. The device automatically obtains an IPv6 address when connected to the network, no manual configuration is required.
SLAAC
SLAAC(Stateless Address Autoconfiguration) is a stateless address automatic configuration method that automatically assigns IPv6 addresses to devices by taking advantage of IPv6 features. In SLAAC, the device receives a network prefix (Prefix) from the router in the network, and then automatically constructs its own IPv6 address based on the prefix.
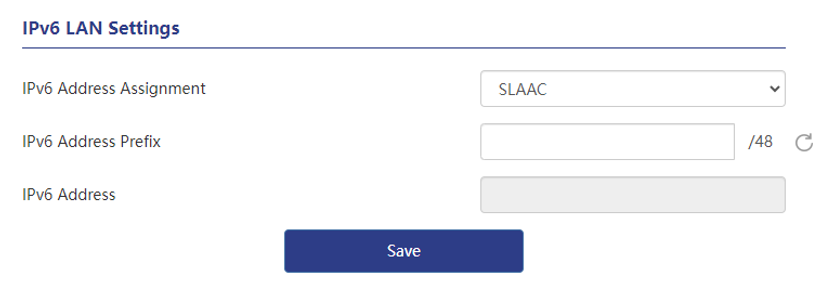
To use SLAAC, you need to ensure that the routers in the network have been configured with IPv6 prefixes and broadcast the prefixes to devices connected to the network. The device automatically generates an IPv6 address based on the prefix, without using DHCPv6 or other configuration.
The difference :
-
Automatic Allocation relies on the DHCPv6 protocol and the configured DHCPv6 server for address allocation, while SLAAC implements automatic address configuration through router broadcast network prefixes.
-
Automatic Allocation requires DHCPv6 configuration and management, while SLAAC does not require additional configuration.
-
Automatic Allocation can provide more flexibility, such as other network information such as DNS server and gateway addresses can be allocated through a DHCPv6 server. SLAAC only provides address configuration, and other network information may need to be obtained through other methods.
Which method to use depends on your network environment and needs. If unsure, it is recommended to contact your network administrator or service provider for accurate configuration information and recommendations.